
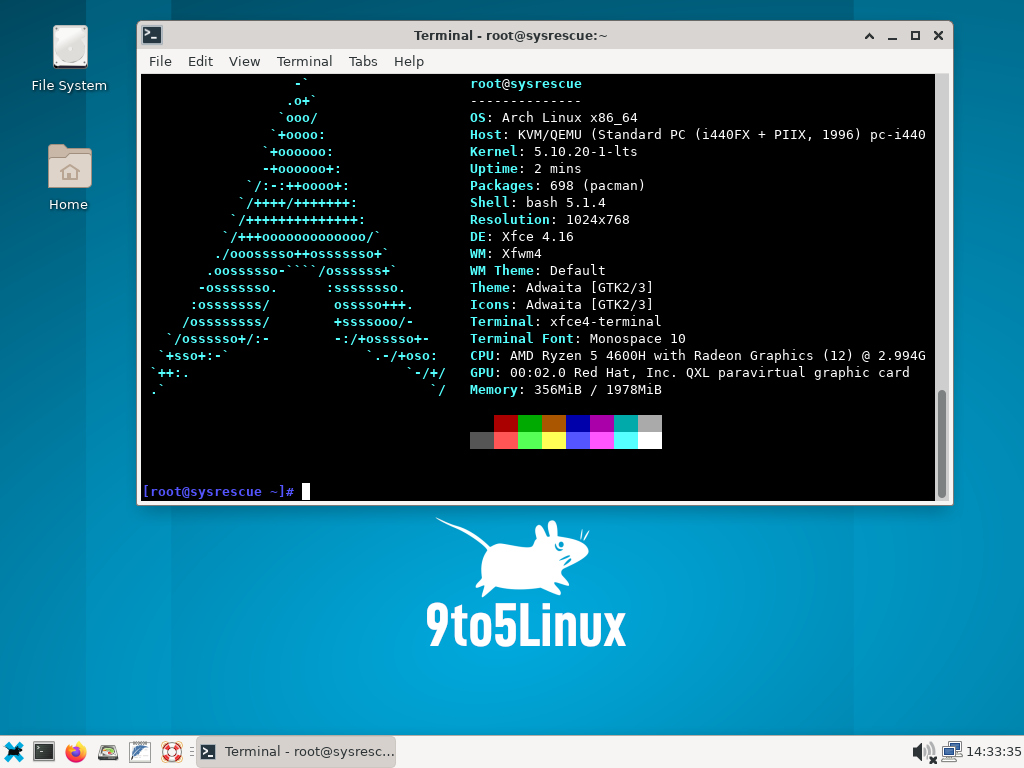
The boot flag needs to be set to the correct partition using either fdisk(a) or parted(b). Make sure that the new root partition has a filesystem on it. To copy at the filesystem level, use an rsync command after mounting both the old and new root partitions. This will ensure that any filesystem is copied in a consistent manner (using dd on a read/write mounted filesystem carries a major risk of introducing corruption on the target device should anything change on the source during the copy process).ī. However, if you do mount any filesystem from the disks to be copied, please ensure that you mount these filesystems as read-only, or remount them as read-only before starting any copy using dd. Important: The disks being copied do not need to be mounted. # dd if=/dev/ of=/dev/ bs=64k conv=noerror,sync NOTE: If the dd command is not being used to copy data from an entire disk to an entire disk, the partition(s) will need to be created prior to this step. Here is an example dd command for copying at the block level:

Make sure the new disk is available.Ĭopy data at the block(a) or filesystem(b) level depending on preference from the old disk to the new disk.Ī. This is the safest way to copy data from the root disk as it prevents a situation where data is changing while we are copying from it. Use the installation media to enter rescue mode on the system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
